IGF-1 Diagnosis
IGF-1 Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Severe Primary IGF-1 Deficiency
Knowing your patients’ insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) level is an important step in the diagnosis of severe primary IGF-1 deficiency (SPIGFD).3 A diagnosis of SPIGFD is made when a child’s IGF-1 concentration is a standard deviation score (SDS) of ≤ -3.0 and their growth hormone (GH) levels are within the normal range or are elevated, and their height is an SDS of ≤ -3.0.1
Short Stature
Short Stature
Endocrine Assessment of a Patient with Short Stature
After the general assessment of a patient with short stature (which may include a review of the patient’s growth history and medical history, physical examination, or general laboratory tests) to investigate other causes, an investigation may then be conducted to assess the growth hormone (GH)-IGF-1 axis prior to the initiation of therapy.3,8
Possible defects in GH and IGF-1 levels1,7
GH, growth hormone; IGF-1; insulin-like growth factor-1; PIGFD, primary IGF-1 deficiency; SPIGFD, severe primary IGF-1 deficiency; SDS, standard deviation score. *Defined by a height of SDS ≤ -3.0, basal IGF-1 SDS ≤ -3.0, and normal or elevated GH.
Clinical Presentations of Primary IGFD
A patient with primary IGFD may exhibit a number of unique clinical features in addition to having short stature, including:6,9
- Hypoglycemia
- Obesity (with abdominal adiposity)
- Undeveloped muscles
- Midfacial hypoplasia
- High-pitched voice
- Osteoporosis
- Small genitalia since birth
- Delayed puberty
Criteria for a Diagnosis of SPIGFD
SPIGFD may be the cause of a severe impairment in growth.1
The diagnosis of SPIGFD is made when a patient meets the following criteria:
- Height standard deviation score (SDS) ≤ -3.0
- IGF-1 concentration SDS ≤ -3.0
- GH is normal or elevated
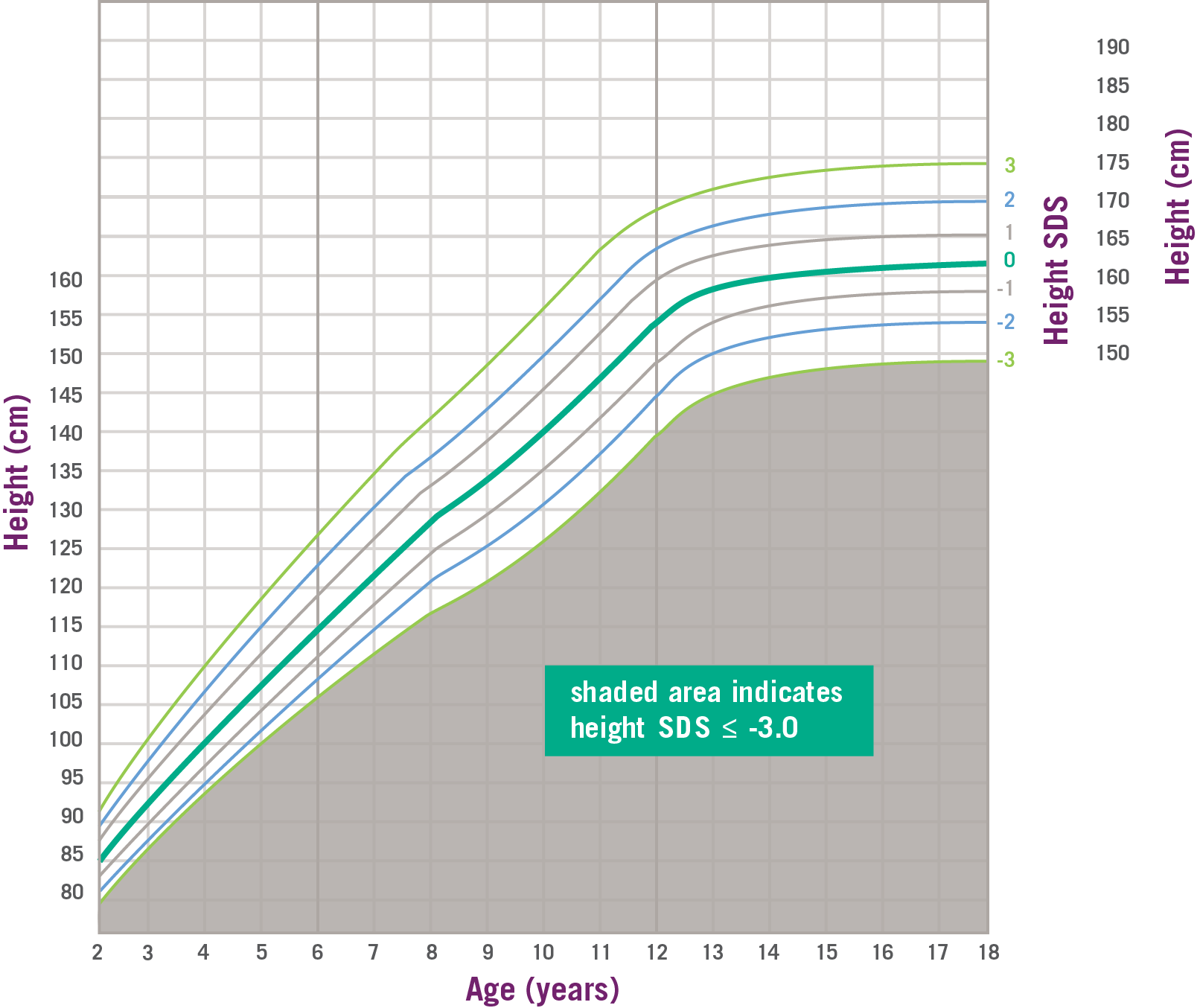
SPIGFD Patients Have Height SDS of ≤ -3.0* 1
Data and formula from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. SDS, standard deviation score. *SPIGFD is defined by a height of SDS ≤ -3.0 (shaded area), basal IGF-1 SDS ≤ -3.0, and normal or elevated GH.1
Proper Diagnosis
Proper Diagnosis
The Importance of a Proper Diagnosis
Testing for severe primary IGF1 deficiency in children with short stature and suspected defect in the GH-IGF-1 axis is essential because these children have a limited time to reach their full growth potential with treatment before epiphyseal fusion. Timely diagnosis allows for the condition to be treated for a longer period prior to epiphyseal fusion.1,3
GH-IGF-1 Axis
GH-IGF-1 Axis
Assessment of the GH-IGF-1 Axis
Tests that may be used to help distinguish SPIGFD from GHD include:10
- GH provocation (stimulation) test
- Circulation levels of GH binding protein (GHBP)
- IGF-1 generation test
- IGF-1 mutation analyses
Monitoring
Monitoring
Monitoring your patients during the course of treatment
In children previously diagnosed with a growth disorder and treated with GH, treatment response may vary by diagnosis, as well as by age and gender. If a child’s growth velocity is tracking below the average on an appropriate growth chart, this may be an indication that additional evaluation or re-evaluation is necessary. This evaluation may include an assessment of compliance, and whether other diagnoses, including SPIGFD, should be considered.